A. Karatutlu, PhD in Physics
Web of Science ResearcherID: B-2171-2019
Original Research Papers
2023
[21] Timuçin Emre Tabaru, Ali Karatutlu, and Bülend Ortaç
Phase-Shifted Bragg-Grating Consisting of Silicon Oxynitride Doped Silicon and Silica Alternating Layers Lab-on-Fiber for Biosensors with Ultrahigh Sensitivity and Ultra-Low Detection Limit 2023, Optics & Lasers Technology DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2023.109693
[20] Ali Karatutlu, Timuçin Emre Tabaru, and Bülend Ortaç
Low-temperature synthesis of Silicon Oxynitride-doped Si for tunable Bragg gratings homogeneously deposited on Si, SiO2 and borosilicate substrates and the tip of SM and PM optical fibers, 2023, Advanced Optical Materials DOI: 10.1002/adom.202300094
2022
[19] Esra Kendir Tekgul, Yakup Midilli, Huseyin Can Çamiçi, Elif Yapar Yıldırım, Ali Karatutlu and Bülend Ortaç Effects of Gamma Radiation on Yb-doped Al-P-Silicate Optical Fibers Applied Physics B: Lasers and Optics 128, 170 (2022) DOI: 10.1007/s00340-022-07891-y
[18] Ali Karatutlu, Elif Yapar Yıldırım, Esra Kendir, Yakup Midilli, Samet Akçimen, Bülend Ortaç Fabrication of Biaxial Polarization-Maintaining Optical Fiber with Ultra-Low Bending-Dependent Polarization Extinction Ratio Deterioration Optical Fiber Technology Volume 69, March 2022, 1028362022 DOI: 10.1016/j.yofte.2022.102836
2020
[17] İ. Seker, A. Karatutlu, K Golcuk, M. Karakiz, B. Ortaç,A Systematic Study on Au-capped Si Nanowhiskers for Size-Dependent Improved Biosensing Applications, Plasmonics, 15:1739–1745 (2020) DOI: 10.1007/s11468-020-01195-7
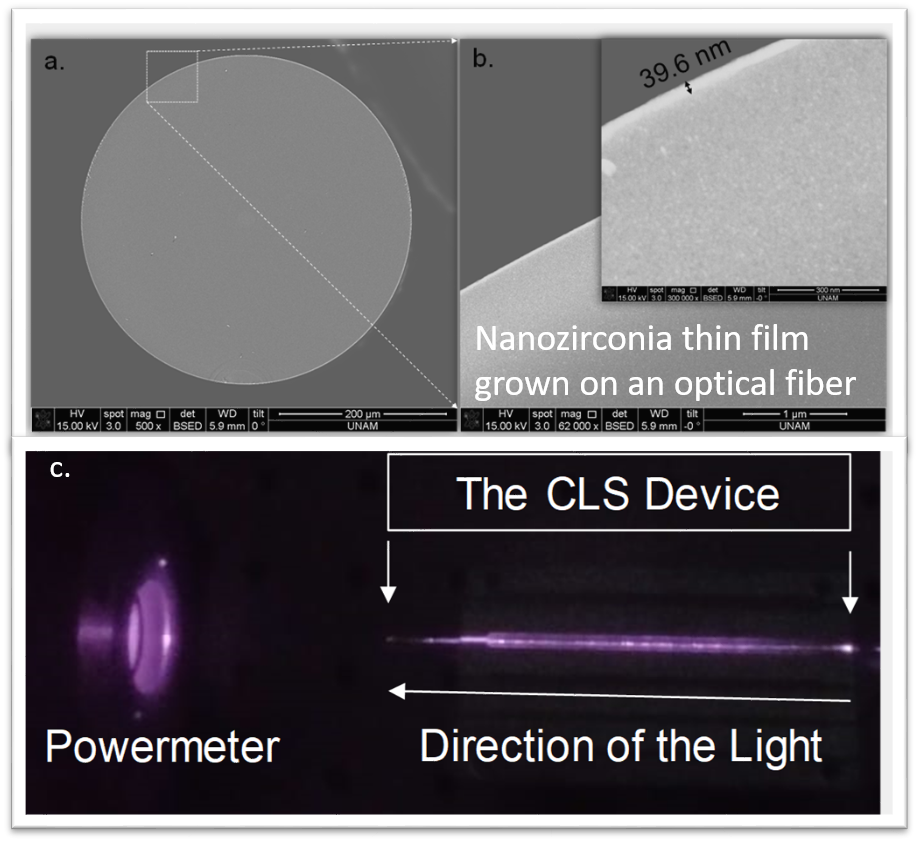
[16] A. Karatutlu, Atomic layer deposition of zirconium oxide thin film on an optical fiber for cladding light strippers, Turkish Journal of Physics, DOI: 10.3906/fiz-1908-6, Available online: 07.01.2020
2019
[15] E. Y. Yıldırım, A. Karatutlu, E. T. Balk, Y. Midilli, B. Ortaç Combined method for the fabrication of high-power cladding light stripper using buffered oxide etchant Applied Optics, Vol. 58, Issue 25,pp. 6926-6933(2019) Click here to read more
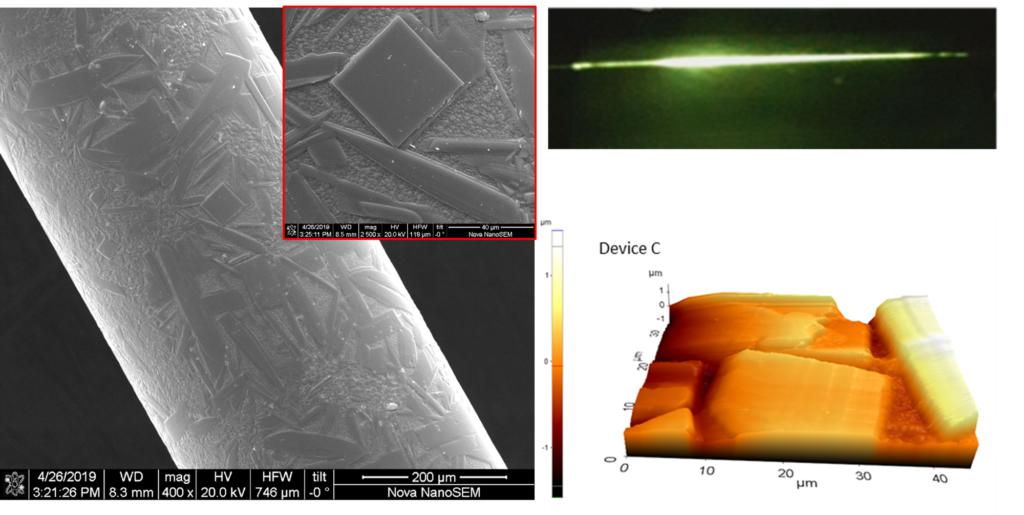
Cladding light strippers are vital and one of the critical components for high-power fiber laser applications. In this study, we show the first studies of the formation mechanisms and optimum conditions of a cladding light stripper(CLS) device using a buffered oxide etchant by a combined method of stain (wet) etching and vapor phase etching.This high-power CLS was shown to result in a stripping performance of ~17.2 dB at the launched power of 333 W(pump limited).
[14] C. Candan, A. A. Seymen, A. Karatutlu, M. Tiken, Y. Midilli, ,E. Orhan, H. Berberoğlu, B. Ortaç Performance Evaluation of Fiber-based Ballistic Composites against Laser Threats, Optics and Lasers in Engineering Volume 121, October 2019, Pages 54-60
Click doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.03.016

In this study, a specially developed composite material for the ballistic applications was shined to a continuous wave (CW) laser beam at 915 nm. At the instant of the exposure, the region of interest was completely evaporated and punctured with a slight swelling around the hole where the temperature was over 450 °C. The composite material was drilled completely upon exceeding 20 kJ of laser energy.
2018
[13] A. Karatutlu, F. S. Boi, R. Wilson, O. Ersoy, B. Ortaç , A. Sapelkin A Bean-like Formation of Nanoparticles inside the Carbon Nanotubes: Colloidal Germanium Nanoparticles Implanted throughout Iron-filled CNTs Crystal Research & Technology 2018-10-22
Click doi: 10.1002/crat.2
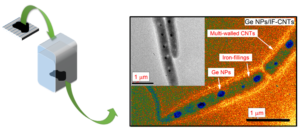 A recipe for a junction of Ge/Fe inside a single CNT is demonstrated with a bean‐like deposition of Ge NPs. The results indicate that Ge NPs and IF‐CNTs demonstrate cocatalytic activity in increasing the respective sizes, which are dramatically larger than those obtained by the conventional approaches.
A recipe for a junction of Ge/Fe inside a single CNT is demonstrated with a bean‐like deposition of Ge NPs. The results indicate that Ge NPs and IF‐CNTs demonstrate cocatalytic activity in increasing the respective sizes, which are dramatically larger than those obtained by the conventional approaches.
[12] A Karatutlu, B Patil, …, A. Sapelkin Structural, Optical, Electrical and Electrocatalytic Activity Properties Of Luminescent Organic Carbon Quantum Dots 3/17 2018 Chemistry Select Click doi: 10.1002/slct.201800714
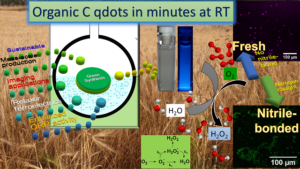 We demonstrate organic carbon quantum dots (qdots) containing nitrile bonded (C≡N bond) d‐glucose‐like traces in various sizes obtained from wheat flour to be promising for imaging applications and to possess a relaxor ferroelectric property and an enhanced electrocatalytic activity that could reduce the cost of energy devices and simple to scale up for the commercialization.
We demonstrate organic carbon quantum dots (qdots) containing nitrile bonded (C≡N bond) d‐glucose‐like traces in various sizes obtained from wheat flour to be promising for imaging applications and to possess a relaxor ferroelectric property and an enhanced electrocatalytic activity that could reduce the cost of energy devices and simple to scale up for the commercialization.
[11] Şeker, İ., Karatutlu, A. & İstengir, S. Preferential MBE Growth and Characterization of SiGe Nanoislands on Depth-Selective Si Pits Etched by Ar + Plasma. Phys. status solidi – Rapid Res. Lett. 1700424 (2018). doi:10.1002/pssr.201700424

Preferential deposition of SiGe nanoislands is selectively demonstrated inside Si nanopits depending on the pit depth. Surface migration plays a role in the deposited Si pits where the selective behavior is surpassed and the SiGe nanoislands are grown all along the Si surface. Such an approach obtained in an MBE system gives the advantage of preparation of different depths and coating thicknesses in situ.
[10] I Seker, A. Karatutlu, O Gurbuz, S Yanik, Y Bakis, M Karakiz (2018) Structural and electrical investigations of MBE-grown SiGe nanoislands App. Phys. A Materials Science & Eng. DOI: 10.1007/s00339-017-1448-6
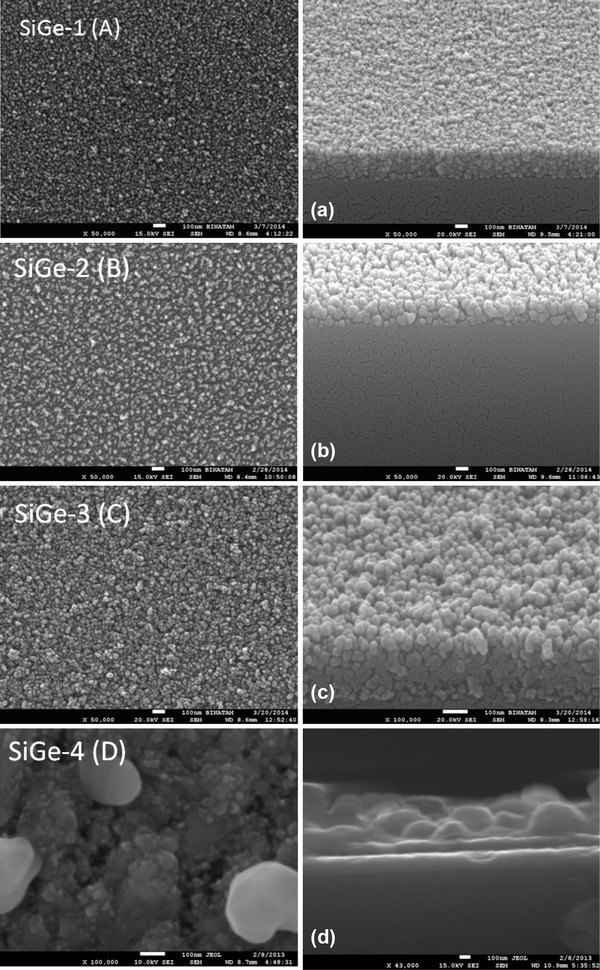
SiGe nanoislands were grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) method on Si (100) substrates with comparative growth parameters such as annealing temperature, top Ge content and layer-by-layer annealing (LBLA).
2017
[9] Karatutlu A, Istengir S, Cosgun S, Seker I, Unal B. Decalin-assisted light emitting porous Si formation and its optical, surface and morphological properties. Appl Surf Sci 2017;422:498–503. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.057.

We report the optimum conditions for production of the most efficient Lep-Si using decalin (decahydronaphtalene) and possible structural origins of light emission using the depth dependent luminescence measurements.
[8] M. Song, A. Karatutlu, I. Ali, O. Ersoy, Y. Zhou, Y. Yang, Y. Zhang, W. R. Little, A. P. Wheeler, and A. V. Sapelkin, “Spectroscopic super-resolution fluorescence cell imaging using ultra-small Ge quantum dots,” Opt. Express, vol. 25, no. 4, p. 4240, Feb. 2017. DOI: 10.1364/OE.25.004240
We demonstrate a spectroscopic imaging based super-resolution approach by separating the overlapping diffraction spots into several detectors during a single scanning period and taking advantage of the size-dependent emission wavelength in nanoparticles. This approach has been tested using off-the-shelf quantum dots (Invitrogen Qdot) and in-house novel ultra-small (~3 nm) Ge QDs.
2016
[7] Zhang, Y., Ersoy, O., Karatutlu, A. & Sapelkin, A. (2016) Local structure of amorphous and nanoscale systems by numerical XANES calculations. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids. 1–6. Click doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.07.001.
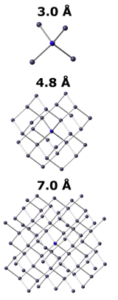 We reproduce the key spectral features in XANES calculations of Ge nanoparticles using the final difference method of FDMNES code. We suggest ways of resolving remaining outstanding issues arising from combination of disorder, size and surface effects.
We reproduce the key spectral features in XANES calculations of Ge nanoparticles using the final difference method of FDMNES code. We suggest ways of resolving remaining outstanding issues arising from combination of disorder, size and surface effects.
2015
[6] Ali Karatutlu, Osman Ersoy, Willim R. Little, Yuanpeng Zhang, Isa Seker and Andrei Sapelkin: Laser-induced particle size tunes and structural transformations in germanium nanoparticles prepared by stain etching and colloidal synthesis route. Journal of Applied Physics 2015 118 (24), 244303 Click doi:10.1063/1.4939066
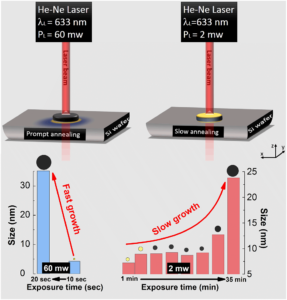 Systematic studies of the laser exposure on Ge nanoparticles prepared by colloidal synthesis results in the fact that the explosive crystallisation is common for H-terminated and partially disordered Ge nanoparticles regardless of its particle size. We suggest possible bio-medical applications for the observed phenomena.
Systematic studies of the laser exposure on Ge nanoparticles prepared by colloidal synthesis results in the fact that the explosive crystallisation is common for H-terminated and partially disordered Ge nanoparticles regardless of its particle size. We suggest possible bio-medical applications for the observed phenomena.
[5] Yuanpeng Zhang, Osman Ersoy, Ali Karatutlu, Andrei Sapelkin: The local structure of Ge quantum dots determined by combined numerical analysis of extended x-ray absorption fine structure and x-ray absorption near-edge structure data. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation 10/2015; 23 (1) Click doi:10.1107/S160057751501913X
The sensitivity of X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) to the local symmetry has been investigated in small (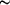 4 nm) matrix-free Ge quantum dots. The FDMNES package was used to calculate the theoretical XANES spectra that were compared with the experimental data of as-prepared and annealed nanoparticles.
4 nm) matrix-free Ge quantum dots. The FDMNES package was used to calculate the theoretical XANES spectra that were compared with the experimental data of as-prepared and annealed nanoparticles.
[4] Niccolo R. C. Corsini, Yuanpeng Zhang, William R Little, Ali Karatutlu, Osman Ersoy, Peter D Haynes, Carla Molteni, Nicholas D M Hine, Jesus Gonzalez, Ignacio Hernandez, Fernando Rodriguez, Vadim V Brazhkin, Andrei V Sapelkin: Pressure-Induced Amorphization and a New High Density Amorphous Metallic Phase in Matrix-Free Ge Nanoparticles. Nano Letters 10/2015; Click doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02627

Here, we report on the remarkable behavior of small (under ∼5 nm) matrix-free Ge nanoparticles under hydrostatic compression that is drastically different from both larger nanoparticles and bulk Ge. We discover that the application of pressure drives surface-induced amorphization leading to Ge–Ge bond overcompression and eventually to a polyamorphic semiconductor-to-metal transformation.
[3] Ali Karatutlu, Mingying Song, Ann P. Wheeler, Osman Ersoy, William R. Little, Yuanpeng Zhang, Pascal Puech, Filippo S. Boi, Zofia Luklinska, Andrei V. Sapelkin: Synthesis and structure of free-standing Germanium quantum dots and their application in live cell imaging. RSC Advances 02/2015; 5(26-26):20566-20573. Click doi:10.1039/c5ra01529d
The structure of the as-prepared Ge quantum dots that were found is best described by a core–shell model with a small crystalline core and an amorphous outer shell with a surface that was terminated by hydrogen-related species. Investigation of toxicity, based on a viability test, of as-prepared uncoated Ge quantum dots in HeLa cells was carried out and compared with the commercial carboxyl coated CdSe/ZnSe quantum dots. The viability tests show that Ge quantum dots are less toxic when compared to commercial carboxyl coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots.
[2] Yuanpeng Zhang, Ali Karatutlu, Osman Ersoy, William Little, Giannantonio Cibin, Andy Dent, Andrei Sapelkin: Structure and effects of annealing in colloidal matrix-free Ge quantum dots. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation 01/2015; 22(1-1):105-112. Click doi:10.1107/S1600577514022486

It was found that as-prepared samples possess distinctly different structures depending on their synthesis route as indicated by their long-range ordering. An appreciable amount of oxygen was found to be bound to Ge in samples prepared with GeO2 as a precursor; however, not for GeCl4.Annealing in an H2Ar atmosphere leads to sample crystallization and further nanoparticle growth, while at the same time reducing the Ge-O bonding.
2014
[1] Little, W., Karatutlu, A., Bolmatov, D., Trachenko, K., Sapelkin, A. V, Cibin, G., Taylor, R., Mosselmans, F., Dent, A.J., Mountjoy, G., 2014. Structural origin of light emission in germanium quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 4, 7372. Click doi: 10.1038/srep07372
We used a combination of optically-detected x-ray absorption spectroscopy with molecular dynamics simulations to explore the origins of light emission in small (5 nm to 9 nm) Ge nanoparticles. Two sets of nanoparticles were studied, with oxygen and hydrogen terminated surfaces.